本文主要对正则法则的总结
what is Regular Expression?
a regular expression is a specific kind of text pattern that you can use with many modern applications and programming languages. You can use them to verify whether input fits into the text pattern, to find text that matches the pattern within a larger body of text, to replace text matching the pattern with other text or rearranged bits of the matched text, to split a block of text into a list of subtexts, and to shoot yourself in the foot.
in short summary:Regex is the string used to match and process text.
the string is created by regular expression language.
The research object of regex: string or text
The research object of regex: string or text. String is a data structure:Like other more data structures: The below three functions are almost taken into consideration in Data structure research.
- Search/Replace
- delete
- Add/insert
Pure text match:—naïve pattern match algorithm and KMP algorithm
match single character
| 元字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| . | 匹配除换行符以外的任意字符 |
| | 字符转义 | |
| \w | 匹配字母或数字或下划线或汉字 |
| \W (大写字母) | 匹配任意不是字母,数字,下划线,汉字的字符 |
| \s | 匹配任意的空白符 |
| \S(大写字母) | 匹配任意不是空白符的字符 |
| \d | 匹配数字 |
| \D | 匹配任意非数字的字符 |
| | | 是一个非常简捷的元字符,它的意思是或 |
| [xyz] | 字符集合。匹配在[]括号中所包含的任意一个字符。 |
| [^xyz] | 负值字符集合。匹配未包含的任意字符 |
| [a-z] | 字符范围。匹配指定范围内的任意字符。例如,’[a-z]’ 可以匹配 ‘a’ 到 ‘z’ 范围内的任意小写字母字符。 |
| [^a-z] | 负值字符范围。匹配任何不在指定范围内的任意字符。例如,’[^a-z]’ 可以匹配任何不在 ‘a’ 到 ‘z’ 范围内的任意字符。 |
| \cx | 匹配由 x 指明的控制字符。例如, \cM 匹配一个 Control-M 或回车符。x 的值必须为 A-Z 或 a-z 之一。否则,将 c 视为一个原义的 ‘c’ 字符。 |
| \f | 匹配一个换页符。等价于 \x0c 和 \cL。 |
| \n | 匹配一个换行符。等价于 \x0a 和 \cJ。 |
| \r | 匹配一个回车符。等价于 \x0d 和 \cM。 |
| \t | 匹配一个制表符。等价于 \x09 和 \cI |
| \v | 匹配一个垂直制表符。等价于 \x0b 和 \cK |
| \xn | 匹配 n,其中 n 为十六进制转义值。十六进制转义值必须为确定的两个数字长。 |
| \n | 标识一个八进制转义值或一个向后引用。如果 \n 之前至少 n 个获取的子表达式,则 n 为向后引用。否则,如果 n 为八进制数字 (0-7),则 n 为一个八进制转义值。 |
| \nm | 标识一个八进制转义值或一个向后引用。如果 \nm 之前至少有 nm 个获得子表达式,则 nm 为向后引用。如果 \nm 之前至少有 n 个获取,则 n 为一个后跟文字 m 的向后引用。如果前面的条件都不满足,若 n 和 m 均为八进制数字 (0-7),则 \nm 将匹配八进制转义值 nm |
| \nml | 如果 n 为八进制数字 (0-3),且 m 和 l 均为八进制数字 (0-7),则匹配八进制转义值 nml。 |
| \un | 匹配 n,其中 n 是一个用四个十六进制数字表示的 Unicode 字符。 例如, \u00A9 匹配版权符号 (?)。 |
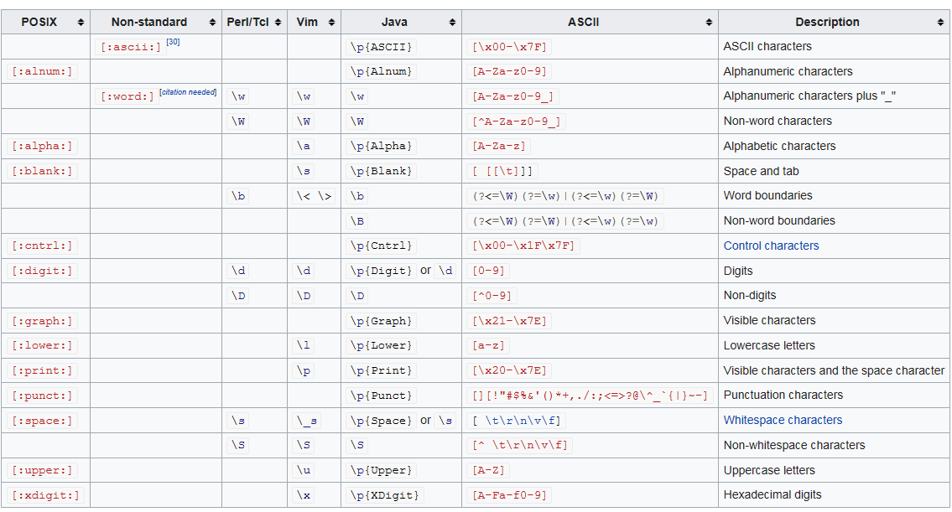
POSIX Character classes
POSIX-Portable Operating System Interface for unix
| 元字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| [:alnum:] | 任何一个字母或数字(等价于[a-zA-Z0-9]) |
| [:alpha:] | 任何一个字母(等价于[a-zA-Z]) |
| [:blank:] | 空格或制表符(等价于[\t]) |
| [:cntrl:] | ASCII控制字符 |
| [:graph:] | 和[:print:]一样,但不包括空格 |
| [:lower:] | 任何一个小写字母(等价于[a-z]) |
| [:print:] | 任何一个可打印字符 |
| [:punct:] | 既不属于[:alnum:]也不属于[:cntrl:]的任何一个字符 |
| [:space:] | 任何一个空白字符,包括空格(等价于[^\f\n\r\t\v]) |
| [:upper:] | 任何一个大写字母(等价于[A-Z]) |
| [:xdigit:] | 任何一个16进制数字(等价于[a-fA-F0-9] |
Repetition Match
| 元字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| “*” | “重复零次或更多次” |
| + | “重复一次或更多次” |
| ? | “重复零次或一次” |
| ?? | 重复0次或1次,但尽可能少重复 |
| *? | 重复任意次,但尽可能少重复 |
| ”+?” | 重复1次或更多次,但尽可能少重复 |
| “{n}” | “重复n次” |
| “{n,}” | “重复n次或更多次” |
| “{n,m}” | “重复n到m次 “ |
| {n,m}? | 重复n到m次,但尽可能少重复 |
| {n,}? | 重复n次以上,但尽可能少重复 |
Boundary constrain character
| 元字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| \b | 匹配单词的开始或结束 |
| \B | 匹配不是单词开头或结束的位置 |
| ^ | 匹配字符串的开始 |
| $ | 匹配字符串的结束 |
eg.
Main string: the cat scattered his food all over the room
Pattern string: cat
Regex: \bcat\b
Sub-expression
capture:
Main String: curve(“w1v1p1r1c1”,”x”)
Pattern string: w([0-9]+)v([0-9]+)p([0-9]+)r([0-9]+)c([0-9]+)
| 元字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| () | “(exp)匹配exp,并捕获文本到自动命名的组里” |
| \num | “匹配 第num个前向引用,其中 num 是一个正整数。对前面所捕获的匹配的引用的第num个引用。” |
| ”(? |
“匹配exp,并捕获文本到自定义名称为name的组里,也可以写成(?’name’exp)” |
| ”(?:exp)” | “匹配exp,不捕获匹配的文本,也不给此分组分配组号” |
| (?=exp) | 匹配exp前面的位置 |
| (?<=exp) | 匹配exp后面的位置 |
| (?!exp) | 匹配后面跟的不是exp的位置(查找前面的) |
| (?<!exp) | 匹配前面不是exp的位置(查找后面的) |
| (?#comment) | “这种类型的分组不对正则表达式的处理产生任何影响,用于提供注释让人阅读” |
Conditional expression
main string: 123-456-7890 Could accept
(123)456-7890 Could accept
(123)-456-7890 Cannot accept
1234567890 Cannot accept
123 456 7890 Cannot accept
| regex:(()?\d{3}(?(1)) | -)\d{3}-\d{4} |
Style :?(backer-ference)true-regex|false-regex Not Regex in all environment can support conditional expression
Regex Options
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| IgnoreCase(忽略大小写) | 匹配时不区分大小写。 |
| Multiline(多行模式) | 更改^和$的含义,使它们分别在任意一行的行首和行尾匹配,而不仅仅在整个字符串的开头和结尾匹配。(在此模式下,$的精确含意是:匹配\n之前的位置以及字符串结束前的位置.) |
| Singleline(单行模式) | 更改.的含义,使它与每一个字符匹配(包括换行符\n) |
| IgnorePatternWhitespace(忽略空白) | 忽略表达式中的非转义空白并启用由#标记的注释。 |
| ExplicitCapture(显式捕获 | 仅捕获已被显式命名的组。 |
Regex Priority
| 优先级 | 元字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \ | 转义符 |
| 2 | (), (?:), (?=), [] | 圆括号和方括号 |
| 3 | *, +, ?, {n}, {n,}, {n,m} | 限定符 |
| 4 | ^, $, \任何元字符、任何字符 | 定位点和序列(即:位置和顺序) |
| 5 | | | 替换,”或”操作 字符具有高于替换运算符的优先级,使得”m|food”匹配”m”“food”。若要匹配”mood”或”food”,请使用括号创建子表达式,从而产生”(m|f)ood”。 |
说明:正则表达式从左到右进行计算,并遵循优先级顺序,这与算术表达式非常类似。 相同优先级的从左到右进行运算,不同优先级的运算先高后低。 上表从最高到最低说明了各种正则表达式运算符的优先级顺序。
C++ std::regex
| methods and classes std::regex | data style | function | match times |
|---|---|---|---|
| std::regex_match | method template | using regular expression to match whole string sequence and capture group | only once |
| std::regex_search | method template | to search sub-sequence and capture group | only once |
| std::regex_replace | method template | to replace sub-sequence matched expression with input replaced text, no capture group | multiple times |
| std::regex_iterator | class template | no capture group,match whole main string and get all matched result | multiple times |
| std::regex_token_iterator | class template | based on token (fourth parameter),could capture group , match whole main string,prefix or suffix | multiple times |